21st December 2023
Fire-Stopping and Passive Fire Protection Strategies
Passive fire protection strategies play a critical role in fire safety, and among them, fire-stopping stands as a key element.
What is Passive Fire Protection?
Passive fire protection (PFP) is the use of fire-resistant materials and design features that help to contain the spread of fire, smoke, and toxic gases in a building. Unlike active fire protection systems like fire alarms and sprinklers which react and respond to a fire, passive fire protection is a constant and acts as a barrier to limit the movement of fire, providing more time for evacuation.
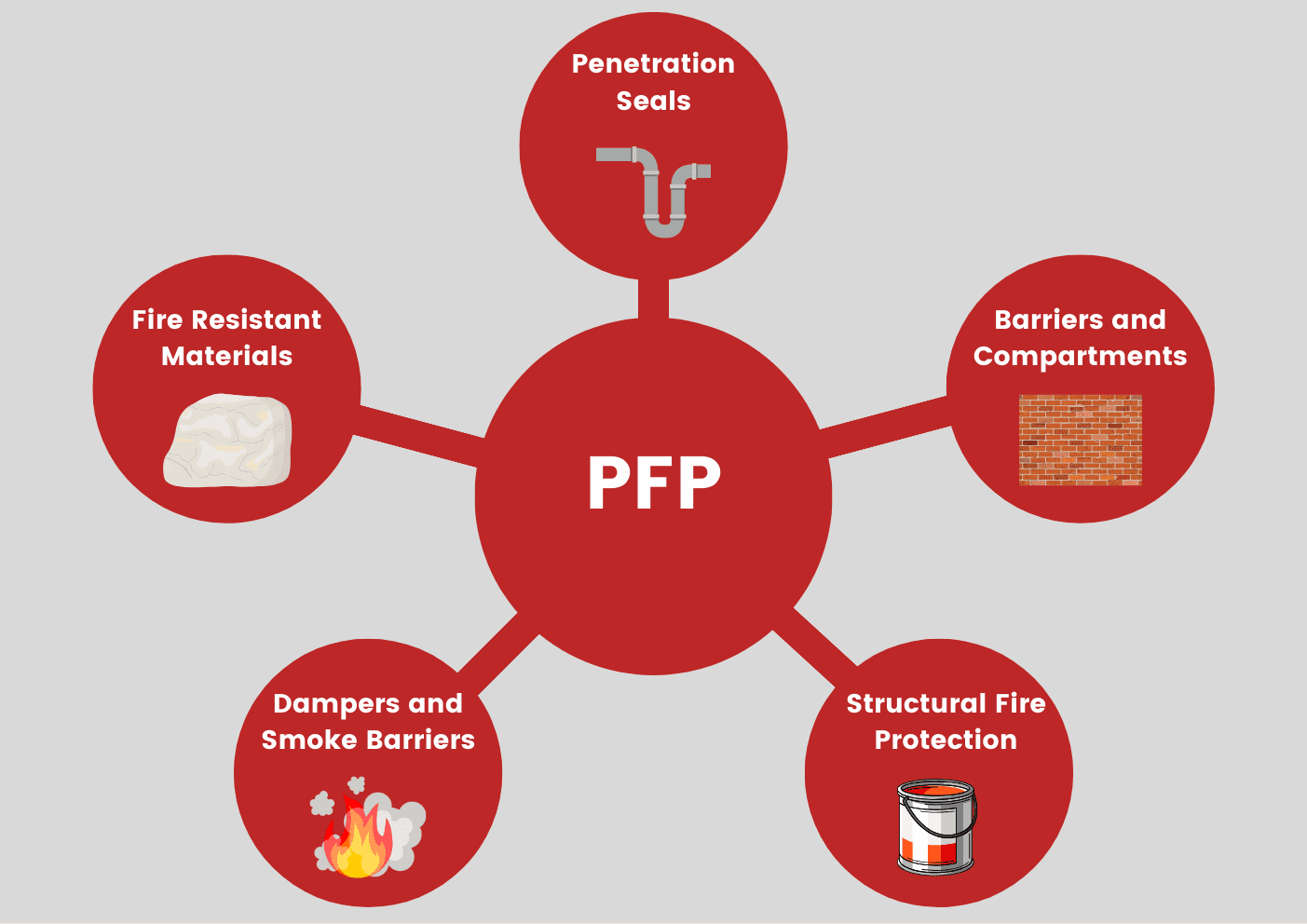
Here are five essential passive fire protection strategies used throughout the industry:
- Fire-Resistant Materials: Materials such as fire-rated walls, floors, and doors constructed from materials like gypsum, concrete, fire-retardant-treated wood, and special coatings. These materials can resist fire for a specified duration, allowing occupants more time to evacuate and firefighters more time to contain fires.
- Compartmentalisation and Fire Barriers: Dividing buildings into compartments, or fire zones, separated by fire-resistant walls and floors can stop the rapid spread of fire and smoke, confining it to limited areas, and preventing it from engulfing the entire structure.
- Fire Dampers and Smoke Barriers: We install fire dampers within heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to prevent the spread of fire and smoke through ductwork. Smoke barriers are fire-rated walls designed to impede smoke movement, aiding in the containment of fire and ensuring safer escape routes for occupants.
- Structural Fire Protection: Using fire-resistant coatings, fireproofing sprays, or intumescent paint on structural components like columns, beams, and load-bearing walls helps to delay the weakening of a building’s structure during a fire.
- Penetration Seals and Firestopping: Seal openings and penetrations in fire-rated walls and floors, such as cable trays, pipes, ducts, and electrical outlets, using fire-resistant materials. Firestopping techniques prevent the spread of fire and smoke through these openings, maintaining the integrity of fire-rated barriers.
Implementing a combination of these passive fire protection strategies is crucial for safeguarding buildings and occupants against the devastating impact of fires, allowing for more effective fire containment and evacuation procedures.
The Role of Fire-Stopping
The role of fire-stopping is fundamental to PFP. Its primary purpose is to seal openings and joints in fire-rated walls, floors, and ceilings, where pipes, cables, ducts, or other services are. Without fire-stopping, these openings can allow fire and smoke to spread rapidly through a building.